Basic Vitamin Facts: B2 (Riboflavin)
Vitamin B2, also called riboflavin, is one of those nutrients you hear about but might not really know. It's a key player in turning food into energy and keeping your cells happy. Let's break down what it is, what it does, and where you can get it.
What Is Riboflavin?
Vitamin B2 is an essential nutrient and one of the eight B-complex vitamins. Because it’s water-soluble, your body doesn't store much of it, so you need to get it from your diet regularly. 4 One of its coolest features is its bright yellow color, which is central to its name. 4

The name "riboflavin" is a mashup of two words. "Ribo" comes from its sugar part (ribitol), and "flavin" comes from the Latin word flavus , which means yellow. 4
Figuring out why riboflavin was important took a while. It started in 1872, when a chemist named Alexander Wynter Blyth noticed a yellow-green glowing pigment in milk whey, which he called "lactochrome". 7 At the time, researchers knew about a "vitamine B" that prevented the disease beriberi, but soon realized it wasn't just one thing. 11
They found a heat-stable part that helped rats grow (that was B2) and another part that fought off beriberi (that was B1, or thiamin). 7 Riboflavin's discovery was weird because it wasn't linked to a big, scary disease like scurvy. 10 Instead, its "growth-stimulating properties" showed it was a key part of how life works, helping with cell growth and energy. 10
How Riboflavin Works
Riboflavin’s main job is to be the starting material for two super important coenzymes, flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). 1 When you eat riboflavin, it gets absorbed and travels to your liver, heart, and kidneys. There, enzymes convert it first into FMN, and then most of that FMN gets turned into FAD. 2
FMN and FAD work like tiny molecular taxis, carrying electrons around in chemical reactions. 6 This job is extra important inside the mitochondria, your cells' power plants. FAD is a crucial part of the electron transport chain, the final step in turning food into usable energy, or ATP. 2, 19
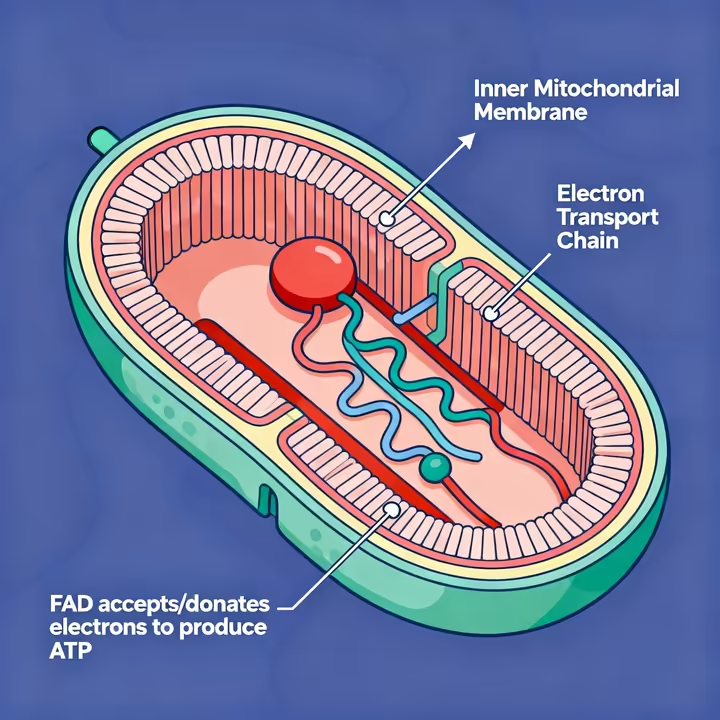
Riboflavin also helps other B vitamins do their jobs. Without it, the whole system gets gummed up. 1 For example, you need an FAD-enzyme to turn tryptophan into niacin (vitamin B3) and an FMN-enzyme to activate vitamin B6. 1 It even helps with folate (B9) and vitamin B12 metabolism, which is why a lack of riboflavin can cause other nutrient deficiencies, too. 13
The Health Perks
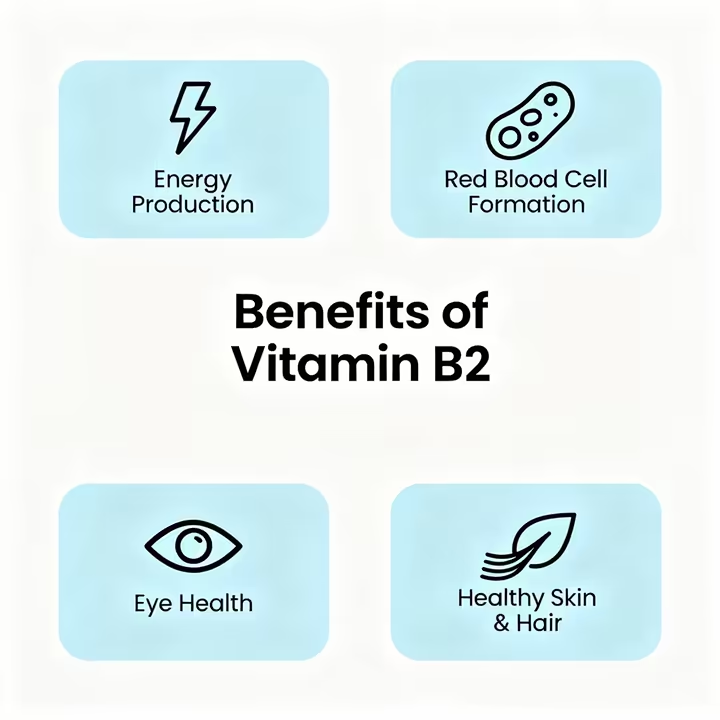
Because riboflavin is so important deep down in your cells, it has a bunch of benefits you can see and feel. These perks are all thanks to the hard work of its coenzymes, FAD and FMN.
Energy and Metabolism
Riboflavin helps turn the food you eat, carbs, fats, and proteins, into energy (ATP). 1 This keeps your metabolism humming and fights off the fatigue and weakness that come from your cells running on empty. 1 It's a key nutrient for staying active and feeling good every day.
Cell Growth and Red Blood Cells
Riboflavin is key for cell growth and repair, especially for making healthy red blood cells. 4, 6 A lack of B2 can mess with how your body uses iron to make hemoglobin, the protein that carries oxygen in your blood. 4 Getting enough riboflavin helps prevent a type of anemia and keeps oxygen moving through your body. 25
Eye Health
Riboflavin helps keep your eyes healthy, particularly the cornea and lens. 2 Getting enough B2 might lower your risk of developing age-related cataracts, a clouding of the lens. 1, 5 Doctors even use riboflavin drops to strengthen the cornea in certain eye conditions, which shows how important it is for your vision. 2
Skin, Hair, and More
Your skin, hair, and the lining of your gut are always renewing themselves, and they need riboflavin for that. 27 That's why a deficiency often shows up as skin problems like a greasy rash, cracked lips (cheilosis), or sores at the corners of your mouth (angular stomatitis). 1
Antioxidant Power
Riboflavin isn't an antioxidant itself, but it plays a big support role. It helps recycle one of the body's most powerful antioxidants, glutathione. 1, 2 Without enough B2, your body can't fight off damage from unstable molecules called free radicals as well. 31
Migraine Prevention
Here's a cool one, riboflavin might help prevent migraines. 1 Studies show that high doses, like 400 mg a day, can reduce how often and how bad migraines get for some people. 5 The theory is that migraines are linked to low energy production in brain cells, and a big dose of B2 helps boost it. 5
Where to Find It
You can get riboflavin from lots of different foods. Dairy is a big one, milk, yogurt, and cheese are packed with it. 5 (Fun fact: milk cartons are opaque to protect the B2 from light, which destroys it!). 5

Organ meats, especially beef liver, are the absolute champions of riboflavin content. 22 Lean meats, chicken, eggs, and some fish like salmon are also great sources. 21 Plus, many countries add riboflavin to grain products like breads and cereals through a process called fortification. 21
If you're plant-based, no worries. Mushrooms (especially portobello), spinach, asparagus, and almonds are good sources. 21, 22 While fruits are good for you, they aren't the best place to look for B2. 33 And since riboflavin is water-soluble, steaming or microwaving veggies is better than boiling to keep the vitamin in your food. 14
How Much Do You Need?
How much riboflavin you need changes with age. Babies need about 0.3-0.4 mg per day. 21 Kids need a bit more, from 0.5 mg for toddlers up to 0.9 mg for pre-teens. 1
For teens and adults, it splits by sex. Teenage boys (14-18) need 1.3 mg, while girls need 1.0 mg. 1 Adult men need 1.3 mg and women need 1.1 mg per day. 5
Pregnancy and Lactation
The need for riboflavin really ramps up during pregnancy and lactation. Pregnant women need 1.4 mg per day to help the baby's bones, muscles, and nervous system grow. 5, 43 Lactating women need even more, 1.6 mg per day, to pass enough on to the baby through breast milk for their own growth. 5, 41
What Happens If You Don't Get Enough?
Ariboflavinosis, or riboflavin deficiency, is pretty rare in places with fortified foods. 5 But when it happens, the signs show up in fast-growing tissues like your skin and mouth.
Signs and Symptoms
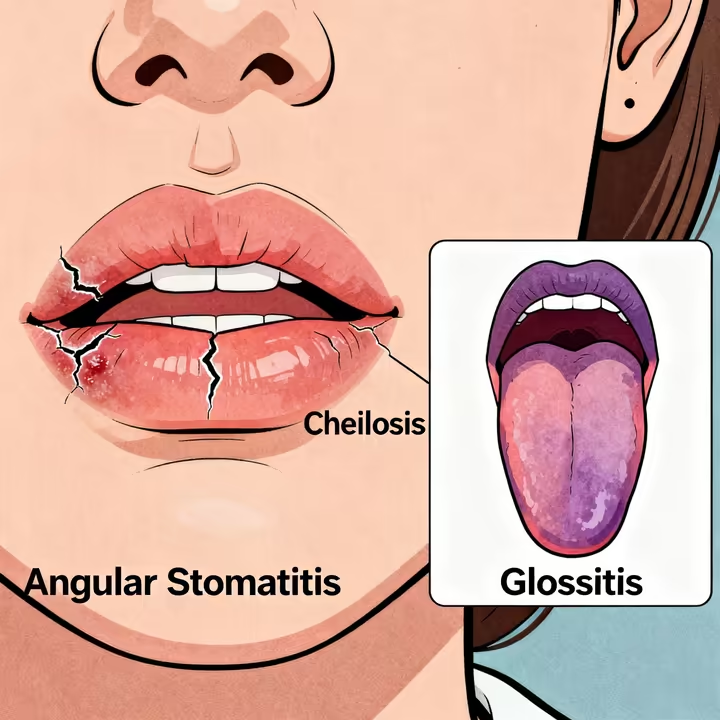
It might start with a sore throat or redness in your mouth. 6 More classic signs are cracked lips (cheilosis), sores at the corners of your mouth (angular stomatitis), and a swollen, purplish tongue (glossitis). 6 You might also get a greasy skin rash (seborrheic dermatitis) or hair loss. 6
Risk Factors
Who's at risk? People with poor diets, chronic alcoholism (it messes with absorption), and conditions like celiac disease. 1, 2 Pregnant women and people with thyroid disease also have higher needs. 5, 21 A very rare genetic disorder also stops the body from using riboflavin properly. 21
Diagnosis
A doctor can often spot the signs. 1 To be sure, they use a blood test called the erythrocyte glutathione reductase activity coefficient (EGRAC) test. 1 (That's a mouthful!) It checks how well a certain enzyme in your red blood cells is working, which depends on riboflavin. 1, 46
Taking B2 Supplements
You can buy riboflavin supplements on their own or in a B-complex or multivitamin. 21 A doctor might suggest them if you have a deficiency, for preventing migraines, or if you have a condition that makes it hard to absorb nutrients. 2
Supplements come in two main forms, regular riboflavin and riboflavin 5'-phosphate (R5P). 2 R5P is the "activated" form, the same as the FMN coenzyme your body makes. 51 For most people, it doesn't matter which one you take, your body converts the regular kind just fine. 36
But... for people with gut issues or other problems that might slow down that conversion, R5P can be better. 51 It's already 'body-ready,' so it might be absorbed and used more easily in those cases.
Is It Safe?
So, can you take too much? Nope, not really. Riboflavin is super safe. 21 Your body has a built-in safety system, you can only absorb so much at one time (about 27 mg). 14
Plus, it's water-soluble, so your body doesn't store large amounts of it. 6 Anything extra is quickly flushed out by your kidneys into your urine. 4 This leads to the most famous side effect, bright, almost neon-yellow pee. 1
This is totally harmless, it's just your body getting rid of the extra B2. Because it's so safe, there is no official "Tolerable Upper Intake Level" (UL) for riboflavin. 5
Playing Well with Others
Riboflavin can interact with some meds. For instance, certain tricyclic antidepressants can block the enzyme that activates riboflavin, creating a deficiency even if you're eating enough. 26, 52 Some antipsychotics and antibiotics can also interfere with it. 1
On the other hand, riboflavin works together with other nutrients. It's needed to process other B vitamins like B3, B6, B9, and B12. 1 It also helps your body absorb and use iron, so getting enough B2 can make iron therapy for anemia work better. 4
Works cited
- Riboflavin Deficiency - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470460/
- Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525977/
- B Vitamins - The Nutrition Source, https://nutritionsource.hsph.harvard.edu/vitamins/vitamin-b/
- Riboflavin - Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Riboflavin
- Riboflavin – Vitamin B2 - The Nutrition Source, https://nutritionsource.hsph.harvard.edu/riboflavin-vitamin-b2/
- Riboflavin - Dietary Reference Intakes for Thiamin, Riboflavin, Niacin, Vitamin B6, Folate, Vitamin B12, Pantothenic Acid, Biotin, and Choline - NCBI, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK114322/
- Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) - Molecule of the Month - February 2018 (HTML version), https://www.chm.bris.ac.uk/motm/vitaminB2/vitaminb2h.htm
- en.wikipedia.org, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Riboflavin#:~:text=The%20name%20%22riboflavin%22%20comes%20from,flavus%2C%20%22yellow%22).
- Riboflavin - Etymology, Origin & Meaning, https://www.etymonline.com/word/riboflavin
- The discovery and characterization of riboflavin - PubMed, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23183293/
- (PDF) The Discovery and Characterization of Riboflavin - ResearchGate, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/233773345_The_Discovery_and_Characterization_of_Riboflavin
- CHAPTER 1: Historical Context of Vitamin B - Books - The Royal Society of Chemistry, https://books.rsc.org/books/edited-volume/1298/chapter/1178498/Historical-Context-of-Vitamin-B
- Riboflavin | Linus Pauling Institute | Oregon State University, https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/vitamins/riboflavin
- Riboflavin - King's College London, https://www.kcl.ac.uk/open-global/assets/open-global-riboflavin-2019.pdf
- FAD Biology: Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide Role in Energy Production - Longevity Box, https://longevitybox.co.uk/blogs/uk-longevity-blog/fad-biology-flavin-adenine-dinucleotide-role-in-energy-production
- From Metabolism to Vitality: Uncovering Riboflavin's Importance in Poultry Nutrition - MDPI, https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2615/13/22/3554
- The Diverse Roles of Flavin Coenzymes - Nature's Most Versatile Thespians - PMC, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2519020/
- pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2519020/#:~:text=Flavoenzymes%2C%20which%20contain%20FMN%20and,denitrification%2C%20and%20sulfur%20respiration).
- Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | PEREGRUNE, https://www.peregrune.com/blogs/science-vitamins/vitamin-b2-riboflavin
- Vitamin B2: Role, sources, and deficiency - Medical News Today, https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/219561
- Riboflavin - Consumer - NIH Office of Dietary Supplements, https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Riboflavin-Consumer/
- 8 Foods High in Riboflavin and Why You Need It - WebMD, https://www.webmd.com/diet/foods-high-in-riboflavin
- 4 Health Benefits of Riboflavin (Vitamin B2), https://health.clevelandclinic.org/vitamin-b2
- The Anemia of Human Riboflavin Deficiency | Blood - American Society of Hematology, https://ashpublications.org/blood/article/25/4/432/73165/The-Anemia-of-Human-Riboflavin-Deficiency
- Anaemia - World Health Organization (WHO), https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/anaemia
- Riboflavin Benefits: Why Your Body Needs Vitamin B2, https://www.verywellhealth.com/riboflavin-benefits-deficiency-and-more-7508278
- Riboflavin (Vitamin B2): Uses & Side Effects - Cleveland Clinic, https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/drugs/19116-riboflavin-tablets
- RIBOFLAVIN: Overview, Uses, Side Effects, Precautions, Interactions, Dosing and Reviews, https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-957/riboflavin
- Riboflavin Deficiency - Nutritional Disorders - MSD Manual Professional Edition, https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/nutritional-disorders/vitamin-deficiency-dependency-and-toxicity/riboflavin-deficiency
- Riboflavin (oral route) - Side effects & dosage - Mayo Clinic, https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/riboflavin-oral-route/description/drg-20065810
- (PDF) Riboflavin (vitamin B2) and oxidative stress: A review, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/260995732_Riboflavin_vitamin_B2_and_oxidative_stress_A_review
- Accepted manuscript This peer-reviewed article has been accepted for publication but not yet copyedited or typeset, and so may b - Cambridge University Press, https://www.cambridge.org/core/services/aop-cambridge-core/content/view/6434B395E5D41953FDF975198679FF59/S0007114521005031a.pdf/riboflavin-is-an-antioxidant-a-review-update.pdf
- B vitamins and folic acid - - - Vitamins and minerals - NHS, https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/vitamins-and-minerals/vitamin-b/
- RIBOFLAVIN (VITAMIN B2 ) - Linus Pauling Institute, https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/sites/lpi.oregonstate.edu/files/riboflavin-flashcard.pdf
- Riboflavin Fact Sheet for Consumers - NIH Office of Dietary Supplements, https://ods.od.nih.gov/pdf/factsheets/Riboflavin-Consumer.pdf
- Riboflavin - Health Professional Fact Sheet - NIH Office of Dietary Supplements, https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Riboflavin-HealthProfessional/
- 40 Best Vitamin B2 Rich Foods, Fruits and Vegetables and Their Health Benefits., https://www.godigit.com/nutrition/vitamin-b2-rich-foods
- Foods High in Vitamin B2: Meats, Eggs, Veggies, and More - GoodRx, https://www.goodrx.com/well-being/diet-nutrition/foods-high-in-vitamin-b2
- Top 10 Foods Highest in Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) - My Food Data, https://www.myfooddata.com/articles/foods-high-in-riboflavin-vitamin-B2.php
- Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) | OpeN-Global - King's College London, https://www.kcl.ac.uk/open-global/biomarkers/vitamin/vitamin-b2/index
- Riboflavin - Nutrient Reference Values - Eat For Health, https://www.eatforhealth.gov.au/nutrient-reference-values/nutrients/riboflavin
- www.nhs.uk, https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/vitamins-and-minerals/vitamin-b/#:~:text=How%20much%20riboflavin%20do%20I,mg%20a%20day%20for%20women
- Riboflavin (vitamin B2) and pregnancy | BabyCenter, https://www.babycenter.com/pregnancy/diet-and-fitness/riboflavin-in-your-pregnancy-diet_672
- Is it safe for pregnant or breastfeeding women to take vitamin B2? - dotFIT, https://www.dotfit.com/content-5753.html
- Can a Riboflavin Deficiency Affect Your Baby? - Needed, https://thisisneeded.com/blogs/pregnancy/can-riboflavin-deficiency-affect-your-baby
- Riboflavin Deficiency - Nutritional Disorders - Merck Manual Professional Edition, https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/nutritional-disorders/vitamin-deficiency-dependency-and-toxicity/riboflavin-deficiency
- Ariboflavinosis: Vit B2 deficiency | Infonet Biovision Home., https://infonet-biovision.org/nutrition-related-diseases/ariboflavinosis-vit-b2-deficiency
- Vitamin B2 Deficiency: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment & Prevention - ACKO Insurance, https://www.acko.com/health-insurance/diseases/vitamin-b2-deficiency/
- Thorne Riboflavin 5'-Phosphate - Mayo Clinic Store, https://store.mayoclinic.com/thorne-riboflavin-5-phosphate.html
- Riboflavin 5 Phosphate Sodium, USP For Compounding (API) - Mountainside Medical, https://www.mountainside-medical.com/products/riboflavin-5-phosphate-sodium-usp-for-compounding
- Riboflavin 5'-Phosphate & Reviews | Thorne, https://www.thorne.com/products/dp/riboflavin-5-phosphate
- MikronährstoffCoach®: Wechselwirkungen / mikronaehrstoffcoach ..., https://www.mikronaehrstoffcoach.com/en/interactions/interaction.45.html
- Inhibition of Riboflavin Metabolism in Rat Tissues by Chlorpromazine, Imipramine, and Amitriptyline - ResearchGate, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/16934657_Inhibition_of_Riboflavin_Metabolism_in_Rat_Tissues_by_Chlorpromazine_Imipramine_and_Amitriptyline
- Riboflavin: Health Benefits, Side Effects, Uses, Dose & Precautions - RxList, https://www.rxlist.com/supplements/riboflavin.htm